It is considered to be one of the most optimizing solutions for the technology era in the field of helping businesses save more than 90% of costs & utilize time and store invoices safely and securely.
In terms of encouraging Transition from Paper Invoices to E-invoices according to Circular 78 & Decree 123 as quickly as possible, each firm had better clearly understand every issue related to e-invoices such as: What is an electronic invoice? What are the conditions of the organization initiating the e-invoice application? Procedure?…. All the information you need to know about the e-invoice is in the article below.
1. What is an electronic invoice?
The definition of an electronic is based on Article 3, Circular 32/2011/TT-BTC issued on March 14, 2011.
1.1 What is an electronic invoice?
Electronic invoice is a collection of electronic data about the sale of goods and provision of services, which are created, made, sent, received, stored and managed by electronic means. An e-invoice is created, created and processed on the computer system of the organization that has been granted a tax code when selling goods and services, then stored on the computers of the parties in accordance with the law on electronic transactions.
1.2 Types of electronic invoices
Electronic invoices include the following types:
1. Export invoice; VAT invoice; bill of sale; Other menus include: stamps, tickets, cards, insurance receipts…;
2. Non-collectible freight, international shipping freight documents, fee-collecting service budget documents…
The form and content of e-invoices are established in accordance with international and relevant laws.
1.3 Principles of using e-invoices
The principles of using e-invoices include:
The invoice number should be determined according to the principle of continuity and chronological order, each invoice number is guaranteed to be made and used only once.
Invoices made in paper form but processed, transmitted or stored by electronic means are not e-invoices. An e-invoice is legally valid if it simultaneously satisfies the following conditions:
There is a reliable assurance of the integrity of the information contained in the e-invoice since the information is generated in its final form, which means the e-invoice itself.
Integrity evaluation criteria is that information of e-invoices are complete and have not been changed, apart from changes in terms of form arising in the process of exchanging, storing or displaying e-invoices.
The information contained in the e-invoice is accessible and usable in its complete form when needed.
1.4 The e-invoice must apply to the following conditions:
a) Name invoice, symbol invoice, symbol sample, ordinal number unitization; Itemize symbols, samples of symbols and ordinal numbers on invoice menus must be edited according to the provisions in Appendix 1 of Circular No. 153/2010/TT-BTC of the Ministry of Finance.
b) Name, address, tax code number of the seller.
c) Buyer’s name, address, tax code number.
d) Name of goods and services; unit, quantity, unit price; to write by number and by letter. For the invoice value-added unit, in addition to the line unit price which is the non-value-added price, there must be a value-added tax line, value-added tax amount, and the total payable amount in numbers and words. .
e) There should include an Electronic digital signature as prescribed by law of the seller; then date, month and year of making and sending invoices. Electronic signature must be in accordance with the law of the buyer in case the buyer is an accounting unit.
g) Invoices are shown in Vietnamese. In case it is necessary to write much more foreign words, the foreign words should be placed on the right side in parentheses ( ) or placed directly below the Vietnamese line. They should be smaller in size than the Vietnamese word. Digits written on invoices are natural numbers: 0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9; after the digit thousands, million, billion, trillion, million billion, billion billion must put a dot (.); If there is a digit after the unit digit, a comma (,) must be placed after the unit digit.
2. Compulsory use of e-invoices in Vietnam
From October 19, 2020, the government issued Decree 123/2020/ND-CP. Specifically, Article 59 of this Decree states:
“1. This Decree takes effect from July 1, 2022, encouraging agencies, organizations and individuals that meet the conditions on information technology infrastructure to apply regulations on electronic invoices and documents before July 1st, 2022.”
Accordingly, the mandatory deadline for application e-invoices nationwide is July 1, 2022.
At the same time, Article 60 of Decree 123/2020/ND-CP clearly states that enterprises and organizations have announced the issuance of invoices, self-printed invoices, and electronic invoices without tax authority’s code or those who have registered to use e-invoices with tax authorities’ codes, purchased invoices from tax authorities before October 19, 2020, are able to continue to use them until the end of June 30th, 2022.
3. What is an e-invoice with authentication code?
E-invoice with authentication code is a kind of electronic invoice issued with an authentication code and an authenticated invoice number by the tax authority through the invoice authentication code-issuing system of the General Department of Taxation.
According to the Tax authority of Vietnam, there are two types of electronic invoices that are circulated at the same time: electronic invoices (according to Circular No. 32/2011/TT-BTC) and electronic invoices with authentication code (according to Decision No. 1209/2015/QD-BTC). Businesses need to understand what an e-invoice with an authentication code is, who can apply an e-invoice with an authentication code, the conditions for businesses to use authentic e-invoices, etc.
In terms of e-invoices with authentication code, the seller will have to digitally sign the invoice when the tax authority issues the authentication code and the authentication invoice number. Enterprises do not need to make a report on the use of invoices for this type.
4. What are the conditions of the organization that initiates e-invoices?
What are the conditions of the organization that creates the e-invoice?
According to Circular 32/2011/TT-BTC: The seller creating an e-invoice must meet the following conditions:
a) Being a qualified economic organization and conducting electronic transactions in tax declaration with tax authority; or an economic organization that uses electronic transactions in banking activities
b) Having locations, information transmission lines, information networks and communication equipment that meet the requirements of exploitation, control, processing, use, preservation and storage of e-invoices
c) Having a team of qualified and capable executives commensurate with the requirements of creating and using e-invoices according to latest regulations.
d) Having an electronic digital signature as prescribed by law
đ) Having software for selling goods, managing customers and providing services connected to accounting software, which ensures that data of e-invoices are automatically transferred to the software (or database) accounting at the time of establishing e-invoices.
e) There are procedures for data backup, data recovery, data archives that meet the minimum requirements for storage quality, including:
The data storage system must meet/be compatible with data storage systems standards;
There is a process for backing up and recovering data when the system has problems: make sure to back up the data of the e-invoice to information carriers or back up all data online.
5. What are the conditions of an intermediary organization that provides e-invoice solutions?
- According to Circular 32/2011/TT-BTC: An intermediary organization providing e-invoice solutions must satisfy the following conditions:
Being an enterprise operating in Vietnam with a Business Registration Certificate - Being an investment recipient or having an investment license of an enterprise investing in Vietnam in the field of information technology or a bank that is entitled to provide electronic transaction services in banking activities.
- There is a software program for creating and receiving e-invoices.
- Making sure that e-invoices meet the prescribed contents.
- Implementing a system to provide information technology solutions to serve the exchange of electronic data between businesses or organizations.
- Having a system of equipment and techniques to ensure the provision of e-invoice solutions to meet business requirements and legal regulations on invoice issuance.
- Being capable of detecting, warning and preventing illegal access or any attack on the network environment to ensure the confidentiality and integrity of data exchanged between the participants.
- Having procedures and practices in place for data backup, data online backup, data recovery; taking backup measures to troubleshoot problems related to data recovery.
- There is a solution to store the results of the transmissions and receipts between the parties: archiving e-invoices with the requirement that electronic data messages must be kept on the system.
- Every 6 months, the intermediary organization providing e-invoice solutions must report in writing to the tax authority: a list of businesses using the organization’s e-invoice solution (including the seller of the e-invoice solution). goods, buyers; the number of used invoices (including: invoice type, invoice symbol, sample symbol, ordinal number).
6. Notice of electronic invoices issuance
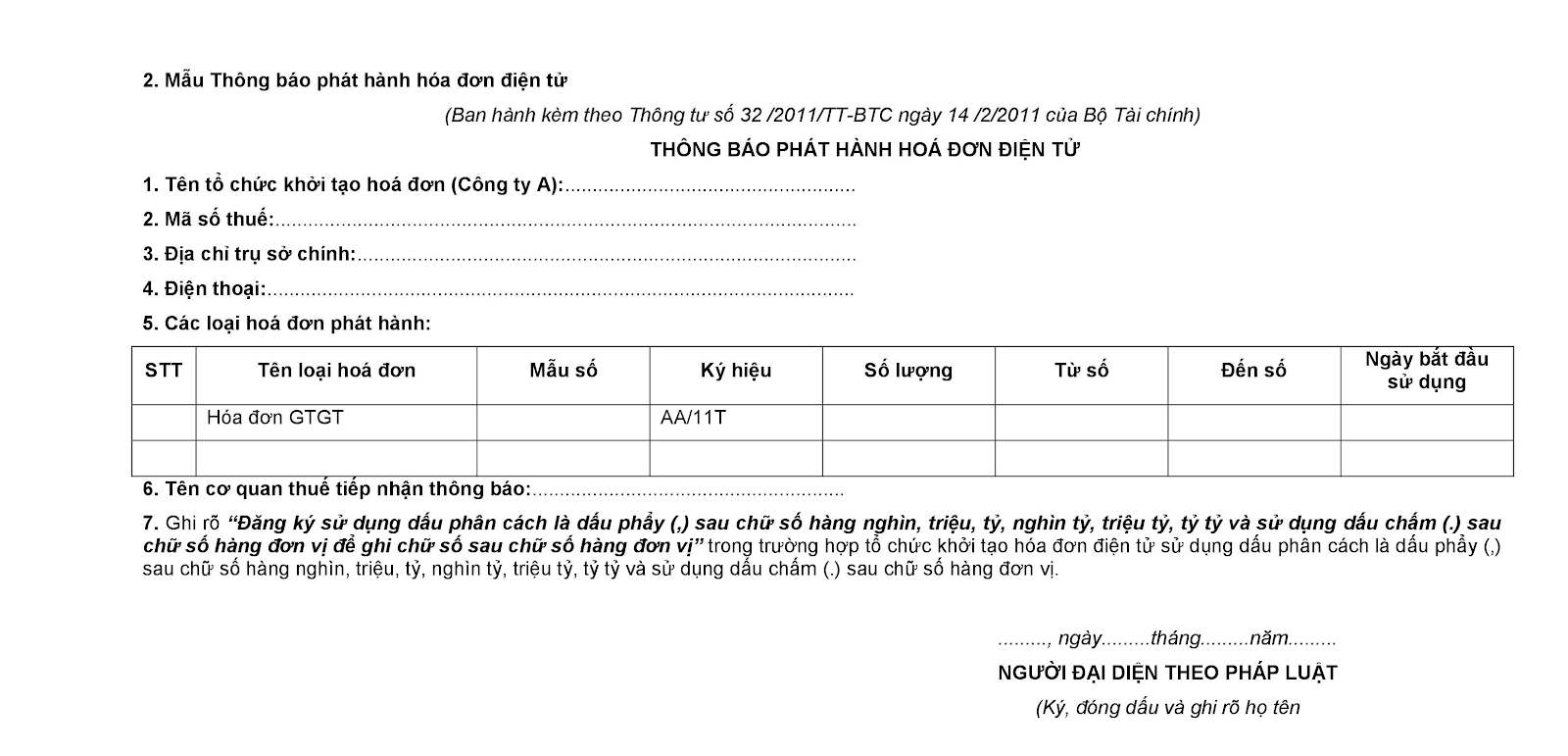
Before creating e-invoices, every organization must complete the procedures for registering e-invoices, including: decision on application of e-invoices, creation of e-invoice templates, and preparation of notices on issuance of e-invoices according to the form of Circular 32/2011/ TT-BTC to be sent to Tax authority directly in paper documents or in electronic documents through the electronic portal.
- Dossier of procedures for notifying the issuance of e-invoices for the first time include:
Notice of issuance of electronic invoices (according to Form No. 2 of Appendix issued together with Circular 32/2011/TT-BTC)
Form No. 2: Notice of electronic invoice issuance (Circular 32/2011/TT-BTC)
Decision on application of e-invoice according to Form No. 1, Appendix issued along with Circular 32/2019/TT-BTC)
Form 01: Decision on the application of electronic invoices (Circular 32/2011/TT-BTC)
- Let’s create a sample invoice in the correct format to send to the buyer, with a digital signature. Businesses can design invoice templates flexibly here!
Before making a dossier, enterprises should contact the tax management officer to know which form of dossier the Tax Department would receive.
Note: After 2 days of sending the notice, if there is no response from the tax authority, the enterprise is allowed to use the e-invoice according to the issuance notice. Enterprises can look up the notice and invoice form at http://tracuuhoadon.gdt.gov.vn.
7. Do electronic invoices have an inter bill?
E-invoice has no concept of inter bill.
Invoice issuer (seller), invoice receiver (buyer) and tax authorities also exploit data on a single e-invoice.
8. In which ways can customers receive e-invoices?
You can send e-invoices directly to the seller by means of transmission and receive e-invoices via Email, SMS
9. Electronic signatures and digital certificates?
9.1. Electronic Signatures
An electronic digital signature is a kind of information accompanying the data (text; images; video…) to identify the data owner; Considered to be an electronic seal of the enterprises, an electronic signature plays an integral part of the e-invoice, which helps to verify the e-invoice is illegal.
An electronic certificate is a data message provided by an organization which offers electronic signature certification services. An electronic certificate is issued to verify that the certified agency, organization or individual is the signer of the electronic signature. Besides, the e-certificate is used to sign the e-invoice, which ensures
Anti-repudiation by signer
The integrity of the e-invoice during storage, transmission and reception
Electronic certificates have a validity period and can be cancelled or revoked by the e-certificate service provider.
9.2. Digital Certificate
A digital certificate is a form of electronic certificate provided by an organization which offers digital signature authentication services. A digital certificate is considered as an “ID card” used in computer and Internet environments.
Digital certificates are used to identify an individual, a server, etc…and attach the object’s identity to a public key. Digital certificates are issued by organizations that have the authority to verify identity and issue digital certificates.
The digital certificate is created by the certificate service provider. Digital certificate contains the user’s public key and the user’s information according to the X.509 standard.
10. Does the buyer have to digitally sign the e-invoice?
– For individual customers & retail customers, there is no need to use e-invoices. In order to declare tax, it is not necessary to electronically sign the e-invoice received
– For corporate customers, the accounting unit needs to use e-invoices to declare tax.
If there are documents of goods and services provision between the seller and the buyer such as economic contracts, delivery notes, delivery notes. receipt of goods, payment records,…, it is not necessary to have the buyer’s electronic signature on e-invoices (according to official dispatch 2402/BTC-TCT dated 23/02/2016)
– For purchase invoices of electricity, water, telecommunications, customers do not need to sign the invoice or have the stamp of the seller. In this case, the invoice is still illegal and accepted by Tax Authority.
– There are also several specific cases where the seller asks the tax authority to accept the buyer without having to digitally sign the invoice.
11. How does the buyer declare tax when receiving the e-invoice?
– After receiving e-invoice from the seller, the buyer can file the tax return, which is similar to the paper invoice’s process.
– The buyer can request the seller to provide an e-invoice which has been converted into paper, signed and stamped from the seller as a document for the settlement file. taxes or shipping documents.
12. Invoices have been issued and sent to the buyer but the goods/services have not been delivered/ the seller and buyer have not declared Tax, what should be done if errors are detected?
The buyer and seller should agree to remove the wrong invoice.
The seller makes an e-invoice to replace the wrong invoice to send to the buyer, on the replacement invoice there must be these words “this invoice replaces the invoice number…, symbol…, sent date…”
Deleted e-invoices must be archived for retrieval of the competent state agency.
13. Invoices have been issued and sent to the buyer, goods & services have been delivered/ the seller and the buyer have declared Tax, then what should be done if errors are detected?
The seller and the buyer must make a written agreement. Agreement is electronically signed by both parties and clearly states the error. At the same time, the seller makes an e-invoice that corrects errors. The latter e-invoice should clearly state the adjustment (increase, decrease) in the quantity of goods, the selling price, and the tax rate. value-added tax, value-added tax for e-invoice number…, symbol…
Based on the adjusted e-invoice, the seller and the buyer will make adjustment declarations according to the provisions of the current law on tax administration and invoices. The adjusted invoice cannot have a negative number (-).
14. With electronic invoices, when goods on the road need to prove their origin, how will transporters have to explain to the competent force?
The seller converts the e-invoice into a paper invoice to prove the origin of tangible goods in the process of circulation. E-invoices converted to paper invoices must fully satisfy the following conditions:
Fully reflect the contents of the original e-invoice;
Invoices must have these words clearly written: BILL IS CONVERTED FROM ELECTRONIC INVOICES
Invoices must have the signature and full name of the person who converts e-invoice to paper invoice.
There should be paper invoices to prove the origin of goods, signed by the legal representative of the seller, and stamped by the seller
15. How to store electronic invoices?
Clause 1, Article 11 of Circular 32/2011/TT-BTC clearly states that in order to store e-invoices, the following steps should be taken:
Sellers and buyers using e-invoices to record accounting books and prepare financial statements must archive e-invoices within the time limit prescribed by the Law on Accounting. In case the e-invoice is created from the system of the intermediary organization, then this intermediary organization must also archive the e-invoice according to the above-mentioned time limit.
If sellers and the buyers are the accounting units and the middle organization, they are responsible for backing up the e-invoice data to information carriers. (For example: a memory stick (USB flash disk); CD and DVD disc; external hard disk; internal hard disk) or perform online backup to protect the data of the e-ID.
The created e-invoice is stored in the form of a data message and must satisfy the following conditions:
The contents of the e-invoice are accessible and usable for reference if necessary
The contents of the e-invoice are stored in the same format in which it was created, sent, received. Moreover, the e-invoice should be stored in the format that allows it to accurately represent the content of the e-invoice.
E-invoices are stored in a certain way that allows identification. origin, destination, date and time of sending or receiving e-invoices.
>> Thus, according to the regulations of the tax authority, invoices after being created need to be archived for the period specified by the Law on Accounting, usually 10 years. Self-printed and ordered invoices may have problems such as data loss, fire or damage of invoices when in its paper form. For e-invoices, burning or damage of invoices is unlikely to happen. Enterprises need to choose electronic invoice software of a reputable supplier with many years of experience in finance and accounting. What’s more, the supplier had better have the most reliable security system.
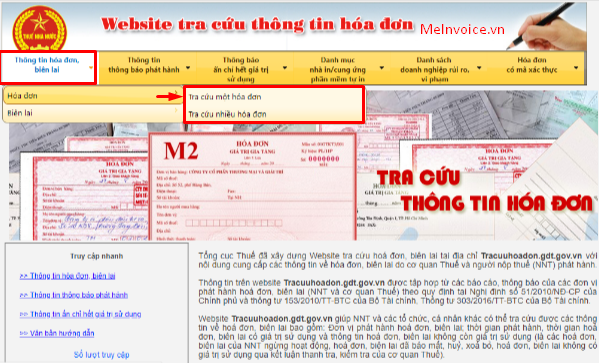
16. Look up valid and legal e-invoices
Looking up the VAT e-invoice on the page of the “GENERAL DEPARTMENT of Taxation” is used in the following cases.
- Case 1: Check and look up VAT e-invoices that have been allowed to use or not. The research should be taken after 2 days from the date of issue of the e-invoice.
- Case 2: Before declaring the enterprise’s accounting invoice, the legitimacy of the invoice should be verified.
Tracuuhoadon.gdt.gov.vn is gathered from reports and notices of invoice and receipt issuers (NNT and tax authorities) in accordance with Decree No. 51/2010/ ND-CP of the Government and Circular 153/2010/TT-BTC of the Ministry of Finance, Circular 303/2016/TT-BTC of the Ministry of Finance.
Specifically, the process of looking up VAT electronic invoices on the General Department of Taxation page includes 3 steps here.
The above is all you need to know about what is an e-invoice? 15 things to know are important information for businesses. Hope you can choose the right e-invoice provider for your business.
MISA meInvoice – The e-invoice software selected by the General Department of Taxation
MISA meInvoice e-invoices are evaluated by Tax Departments and Tax Department nationwide for top quality. MISA meInvoice is used by the largest number of businesses today. The software completely changes the way to issue, manage invoices for more than 150,000 businesses:
- Digitally sign, issue, manage e-invoices ANYWHERE on: Mobile, Desktop, Website
- Decentralize & allow individuals to issue invoices & look up at different locations
- Inheriting data from more than 60 accounting, sales and administration software to issue invoices
- Automatically aggregate invoice reports, VAT declarations & export data easily…
Accompanying Tax Department, Tax Department in the process of converting electronic invoices. MISA Joint Stock Company supports businesses as follows:
1. Exchange paper invoices for electronic invoices
2. Waiver of 5 types of fees up to 5 MILLION:
- 100% free annual subscription fee
- 100% free basic invoice template design
- 100% FREE integration fee with different accounting, sales and administration software
- 100% FREE consultation fee on registration procedures for using e-invoices with Tax Authorities
- 100% FREE storage fee, 10 year invoice lookup
Interested in MISA meInvoice & want a FREE trial with full features for 7 days, please contact Hotline: 090 488 5833 or REGISTER here:














![[Mới] Hướng dẫn 03 cách tra cứu hóa đơn điện tử theo Thông tư 78 và NĐ123 tra cuu hoa don dien tu](/wp-content/uploads/2020/11/tra-cuu-hoa-don-dien-tu-218x150.png)